About ISO/TC204 Intelligent Transport Systems¶
Overview¶
Since our establishment in 1992, TC204 has developed and maintained a suite of standards and other artefacts for the Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) environment. The ITS environment interacts with many other domains and TC 204 coordinates with other ISO technical committees (e.g., TC 22) to ensure a proper division of work as defined by our scope.
ISO / TC 204 standardizes all aspects of information and communication technologies (ICT) for the control, operations and management of surface and near-surface transport systems. This scope covers pedestrians as well as private, public, and commercial movement of people and goods using roads, bridges, tunnels, ferries, motorways, micromobility, public-area mobile robots (PMRs), low-flying aerial vehicles, motorized and non-motorized vehicles, and various driving automation systems within indoor, outdoor, urban, rural, intermodal, and multimodal environments.
The scope includes, but is not limited to, the following service domains and technical aspects: traveller information, traffic management and operations, vehicle services, freight transport, public transport, emergency service, payment for transport-related services, weather and environmental conditions monitoring, disaster response management and coordination, performance management.
Excluded:
- In-vehicle information and control systems and services that are independent of any (1) external data perceived by on-board sensors, or (2) information received via communications with external sources (ISO/TC 22)
Note:
- ISO / TC 204 is responsible for the overall system and infrastructure aspects of intelligent transport systems (ITS), as well as the coordination of the overall ISO work programme in this field including the schedule for standards development, taking into account the work of existing international standardization bodies.
- ISO/TC 204 has developed ISO 14813-1 to formally describe the covered service domains.
To date, we have published over 360 documents that collectively describe broad swaths of the ITS domain. This work exists within a much broader operating context requiring collaboration with other developers of related standards, both within ISO (such as TC22 Road Vehicles and TC344 Innovative Logistics) and beyond (such as CEN/TC278 ITS Standards and ISO/IEC JTC 4 Smart and sustainable cities and communities). We currently have liaisons with roughly 40 other groups.
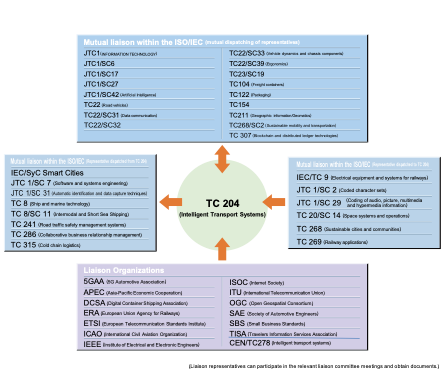
TC 204 Liaisons
TC204 Committee Structure¶
TC204 executes its official work programme through a broad range of groups consisting of:
- AHG - Ad-hoc Groups, which are short-lived groups to advise the TC regarding specific issues
- AG - Advisory Groups, which are standing groups that advise the TC on long-term subjects
- WG - Working Groups, which develop standards and other formal publications of TC 204
- JWG - Joint Working Groups, which formally collaborate with experts outside of TC204 in their development of standards and other documents. JWGs are hosted by a specific TC, but generally have co-chairs from each participating TC.
Our structure is shown below together with our participating and observing members. All of TC204’s groups and convenors may be approached via the TC204 Secretariat.
Scope of TC204 Working Groups¶
TC204's current active groups and their purposes are outlined below.
- AG 2: Identifiers
- AG 3: Operational improvement group
- AG 4: Program coordination
- AG 5: Publication and marketing review
- AHG 2: ITS CyberSecurity
- JWG 1: City data model — Transport
- WG 1: Architecture
- WG 3: ITS geographic data
- WG 5: Fee and toll collection
- WG 7: General fleet management and commercial/freight
- WG 8: Public transport/emergency
- WG 9: Integrated transport information, management and control
- WG 10: Traveller information systems
- WG 14: Driving automation and active safety systems
- WG 16: Communications
- WG 17: Nomadic Devices in ITS Systems
- WG 18: Cooperative systems
- WG 19: Mobility integration
- WG 20: Big Data and Artificial Intelligence supporting ITS
- TC 211 JWG 11: GIS-ITS
Naming Convention for TC204 Deliverables¶
Our document titles may seem a little daunting, however they typically use the multi-level naming structure:
<Publishing SDO(s)>/<Deliverable Type> <Number[-Part]>:<Year of Publication>[(<language>)] <Title 1> - <Title 2> [ - <Title 3>]
Example
ISO/TS 14813-1:2015(en) Intelligent transport systems — Reference model architecture(s) for the ITS sector - Part 1: ITS service domains, service groups and services
| Name Component | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Publishing SDO(s) | ISO | The Standards Development Organisation(s) that will publish the deliverable |
| Deliverable Type | TS | The type of deliverable |
| Number[-Part] | 14813-1 | Unique identifier of the deliverable, which can include an optional Part number to indicate they are focussed components detailing a specific aspect. This can also facilitate progressive development and publishing and use of a suite of documents over time. |
| Year of Publication | 2015 | Year that the deliverable is formally published and released for use |
| language | en | Used to distinguish between English and French editions of a document |
| Title 1 | Intelligent transport systems | Used for most TC204 deliverables |
| Title 2 | Reference model architecture(s) for the ITS sector | Key concept |
| Title 3 | Part 1: ITS service domains, service groups and services | An optional component, but frequently used in order to describe specific aspects of the Key concept. Note that “Part 1: “ is considered part of the title |
