Fee and toll collection (ISO TC 204 WG 5)¶
Introduction¶
Fees and tolls in the road transport sector are used around the world to raise revenue, manage congestion and internalize transport costs, often with the aim of contributing to more sustainable road transport.
Electronic fee collection (EFC) is the general term used to designate ICT solutions that automatically, and without stopping, collect road user fees and tolls. EFC is the general title assigned to ISO publications in the field of road fee and toll collection. EFC systems support efficient charging of road vehicles and a broad variety of pricing policies.
Currently, there are three main technologies used in EFC:
- Dedicated short-range communication (DSRC)
- Autonomous GNSS-based systems
- Image recognition-based systems (incl. ANPR aka ALPR)
Domain of interest¶
The purpose of WG 5 is to:
- support interoperable electronic fee collection (EFC) products and services,
- ease the implementation and operation of EFC schemes and services,
by providing standards that support road user charging transport- and vehicle-related fees and access control (including fee collection for parking lots and ferries) and associated processes (end-user compliance checking, localization augmentation communication, OBE configuration and personalization, system testing and conformity assessment etc.).
WG 5 activities include elaboration of standard documents for:
- reference architecture and related aspects (e.g. enterprise view, vocabulary, data dictionary)
- information security framework, guidelines for protection profiles and security-related mechanisms (data authentication, access credentials, key derivation…)
- DSRC application interface for fee collection and personalization of on-board equipment (OBE), end-user compliance checking and localization augmentation communication etc.
- autonomous (GNSS/CN-based) EFC
- image recognition-based EFC (incl. ANPR aka ALPR) and end-user compliance checking
- information flows between EFC operators (back-office communication between toll chargers and toll service providers)
- performance indicators - metrics and examination framework
- system and application interface conformity-related assessment
WG 5 also:
- reviews interference studies and investigates interferences of other wireless communication media to DSRC, either on its own or in collaboration with other WGs/standardization bodies,
- reviews, investigates and elaborates standard documents for road transport-related payment means and services (e.g. user identification and payment means based on integrated circuit(s) cards, common transport payment means, EFC as an instrument to support traffic management). This is also performed in collaboration with or support to other WGs/standardization bodies.
EFC standardization¶
EFC standards provide solid technical support for agreements between stakeholders (toll chargers and toll service providers) and underpin the interoperability between EFC systems.
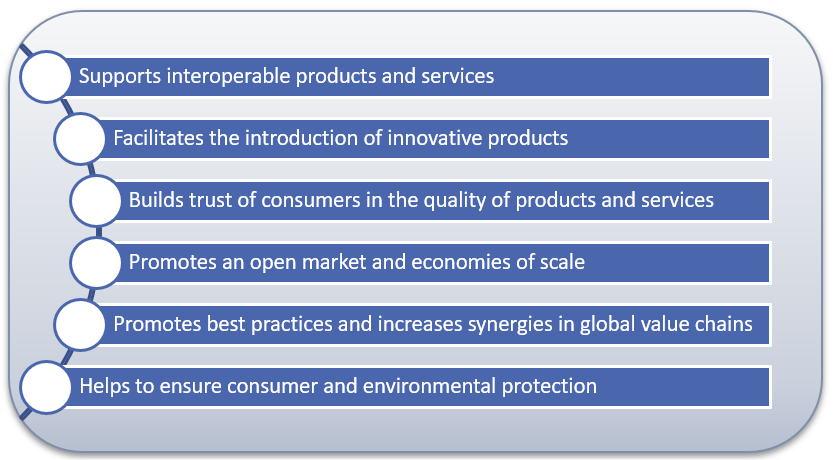
Benefits of EFC standards
ISO/TC 204/WG 5 is responsible for international standardization of the EFC application, whilst other international standardization groups develop technology-related standards (such as GNSS and communication technologies). Most EFC standards are developed as joint work items with CEN/TC 278/WG 1, which is responsible for standardization at European level. In addition, ETSI provides certain technical standards on testing that are relevant for EFC.
Standardization in WG1 can be divided into the following areas:
- Technology-independent standards (e.g. architecture, security and information flows)
- Technology-dependent standards (DSRC-, image recognition- and GNSS-based systems)
Overview of EFC standards¶
WG 5, jointly with CEN/TC 278/WG 1, has produced a series of standards, technical specifications and technical reports. These documents can be purchased from ISO or national standardization bodies.
Click for a standard preview (which links to the Online Browsing Platform, which in turn provide links to on-line store for purchase of the document) or to download machine-readable files (MRFs, e.g. ASN.1 code).
Standards and technical specifications (incl. CEN only)¶
| Technology-independent | Technology-dependent | |
|---|---|---|
| Frameworks | ISO 17573 -1 Architecture | ISO 21719-1 OBE personalization |
| ISO 17573-2 Vocabulary | ||
| ISO 17573-3 Data dictionary [ASN.1] | ||
| ISO 17574 Security profiles | ||
| ISO 19299 Security framework | ||
| Toolboxes | ISO 12855 Information exchange between TC and TSP [ASN.1] | ISO 14906 DSRC application interface [ASN.1] |
| ISO/TS 37444 Charging performance | ISO 16785 Interface between DSRC-OBE and external in-vehicle devices [ASN.1] | |
| ISO/TS 21192 EFC for traffic management [ASN.1] | ISO 25110 DSRC-ICC application interface | |
| ISO/TS 21193 EFC using common media [ASN.1] | ISO 17575 AID for Autonomous EFC [part1][part2][part3][ASN.1] | |
| CEN/TS 16702 Secure monitoring [part1][part2][ASN.1] | ||
| Profiles | EN 16986 IAP for information exchange between TC and TSP [MRFs] | EN 15509 IAP for DSRC EFC [ASN.1] |
| ISO/TS 21719 OBE personalization [part1] [part2] | ||
| ISO 12813 Compliance check communication (CCC) [ASN.1] | ||
| ISO 13141 Localization augmentation communication (LAC) [ASN.1] | ||
| Tests | CEN/TS 17154 Tests against 16986 [part1] | ISO 14907-1 Test procedures for user and fixed equipment |
| ISO 14907-2 OBU tests against 14906 | ||
| EN 15876 Tests against 15509 | ||
| CEN/TS 18078 RLAN interferences to DSRC | ||
| ISO 13143 Tests against 12813 | ||
| ISO 13140 Tests against 13141 | ||
| ISO 16407 Tests against 17575-1 [part1][part2][TTCN] | ||
| ISO 16410 Tests against 17575-3 [part1][part2][][TTCN] |
Contact us¶
Want to know more or participate? Please contact us.

Relationships to other standards:
External References¶
- The European Union- ITS Communications & Information Protocols (EU-ICIP) is a significant resource of ITS standards, and its EFC Tolling page is of particular relevance to this WG's work.
- Introduction to EFC standards
- CO2-based tolling – Eurovignette Directive and EFC standards